Designing Machine learning platforms
Table of Contents
- [Overview of Search Rank Chapter from educative.io and other sources:](#overview-of-search-rank-chapter-from-educative-dot-io-and-other-sources)
Overview of Search Rank Chapter from educative.io and other sources:
Problem: Design a Twitter Feed system that will show the most relevant tweets for a user based on their social graph
-
Time stamp based approach: All tweets gneerated by a users’ followees since user’s last visit were displayed in reverse chronological order.
-
WE need to rank the most relevant tweets:
-
Scale:
- 500 million DAU and on average each user is connected to 100 users.
- Each user fetches their feed 10 times in a day.
500 min * 10 = 5 billion times ranking system will run.
“Given a list of tweets, train an ML model that predicts the probability of engagement of tweets and orders them based on that score”
-
Goal: Maximize user engagement.
-
User actions can be positive or negative
- Postive actions:
- Time spent viewing the tweet
- Liking
- Retweeting
- COmmenting
- Negative Actions:
- Hiding a tweet
- reporting tweet as inappropriate
- Postive actions:
-
User engagement Metrics:
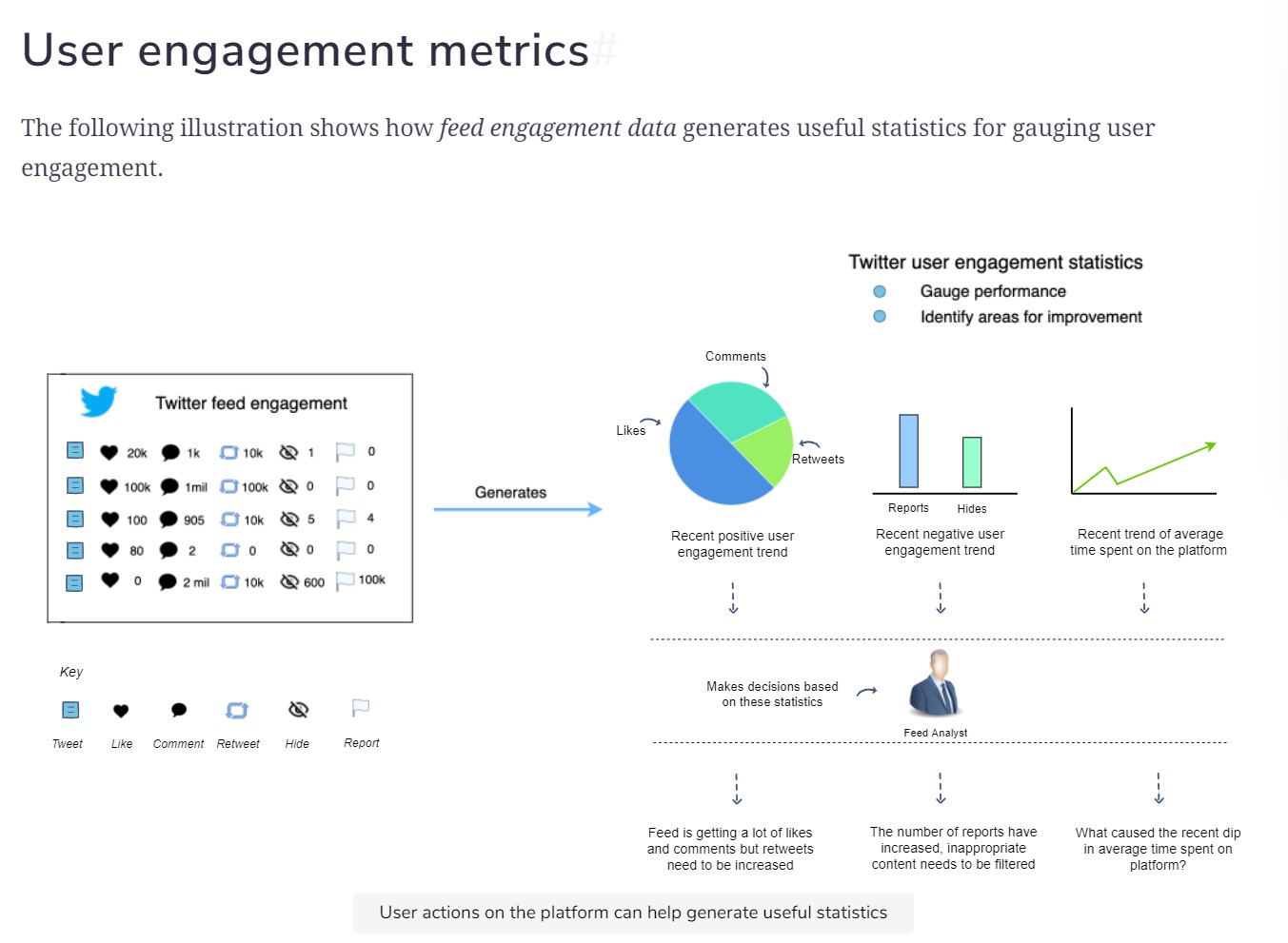
- Increase User engagement:
- Focus on increasing number of comments
- increase overall engagement i.e comments, likes, and retweets
- Increase time spent on twitter
- Average negative action per user
- All engagements are not equally important. So have different weights for each action.
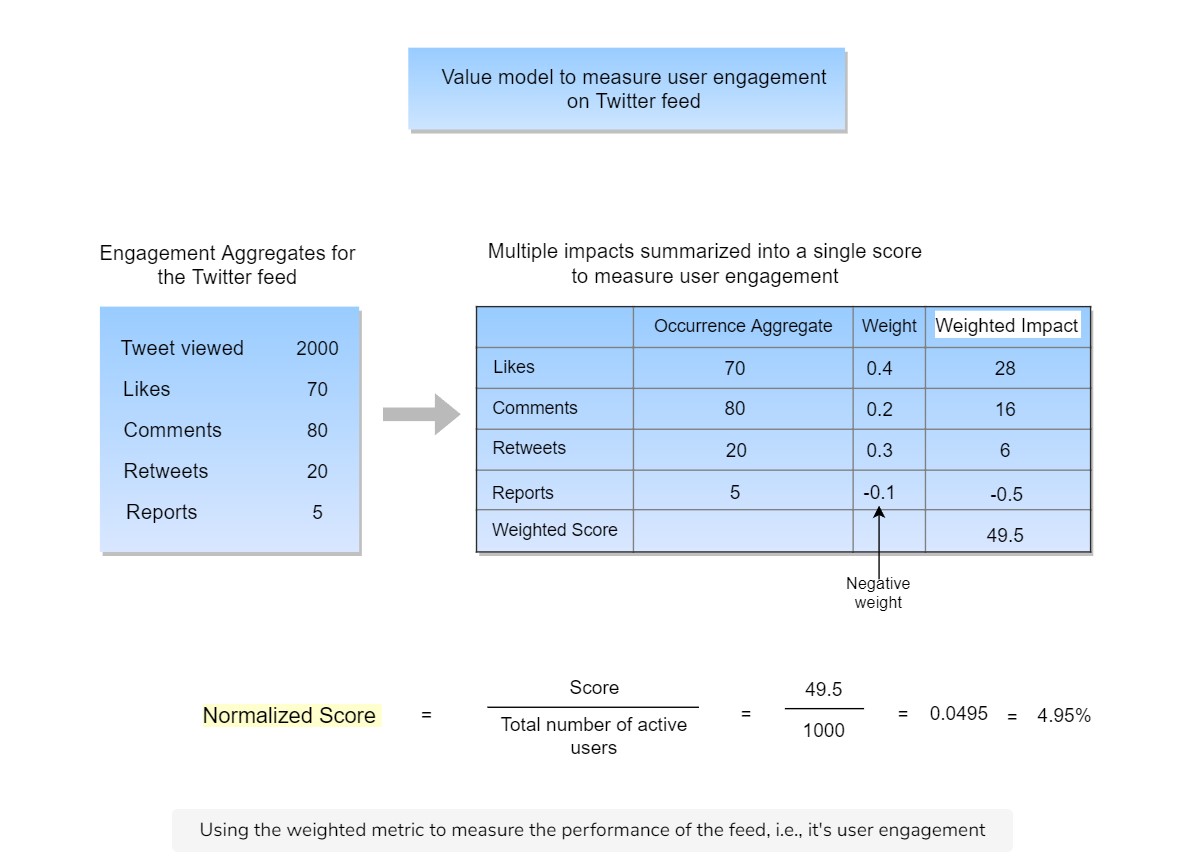
The above metric is calculated as follows:
- IN a day, 2000 tweets were viewed.
- There were 70 likes, 80 comemnts, 20 retweets and 5 reports.
- The wegithed impact is calcuated by multiplying the occurence by their weights.
- The weighted impact is summed up to determine the score.
- The score is normalized with the total number of users.
Why normalization is important?
- The score is caculated for a period of time for a given number of users. If the score is calculated for a different period for different number of users, then the scores will not be comparable.
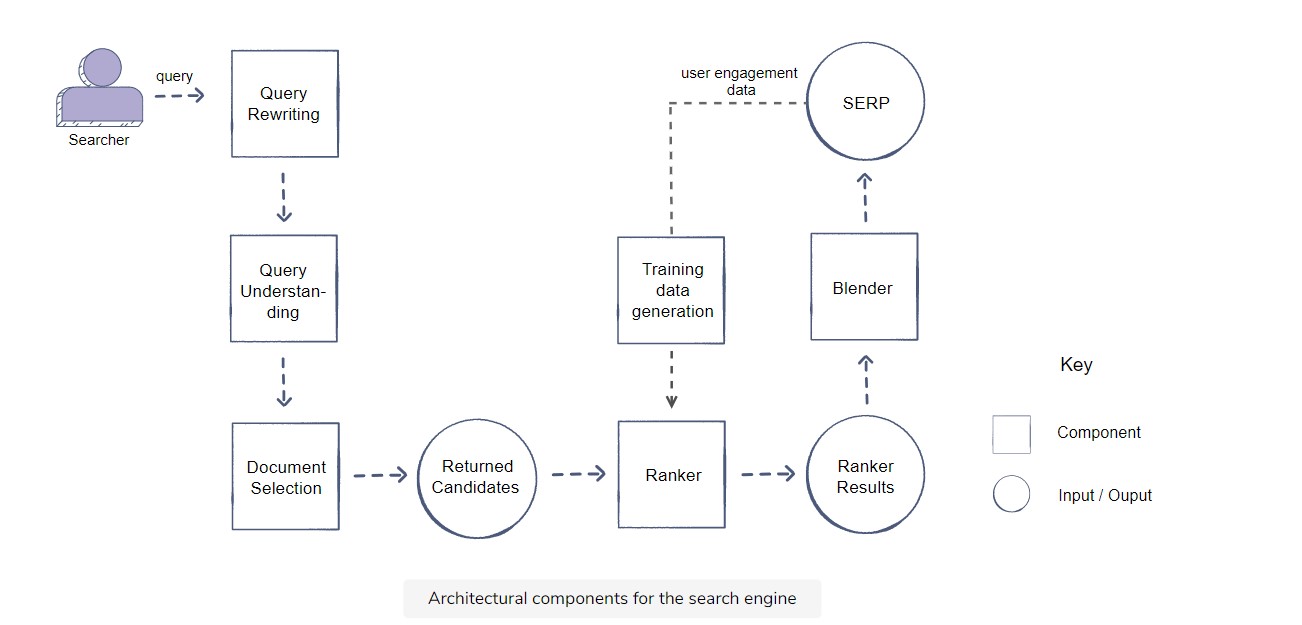
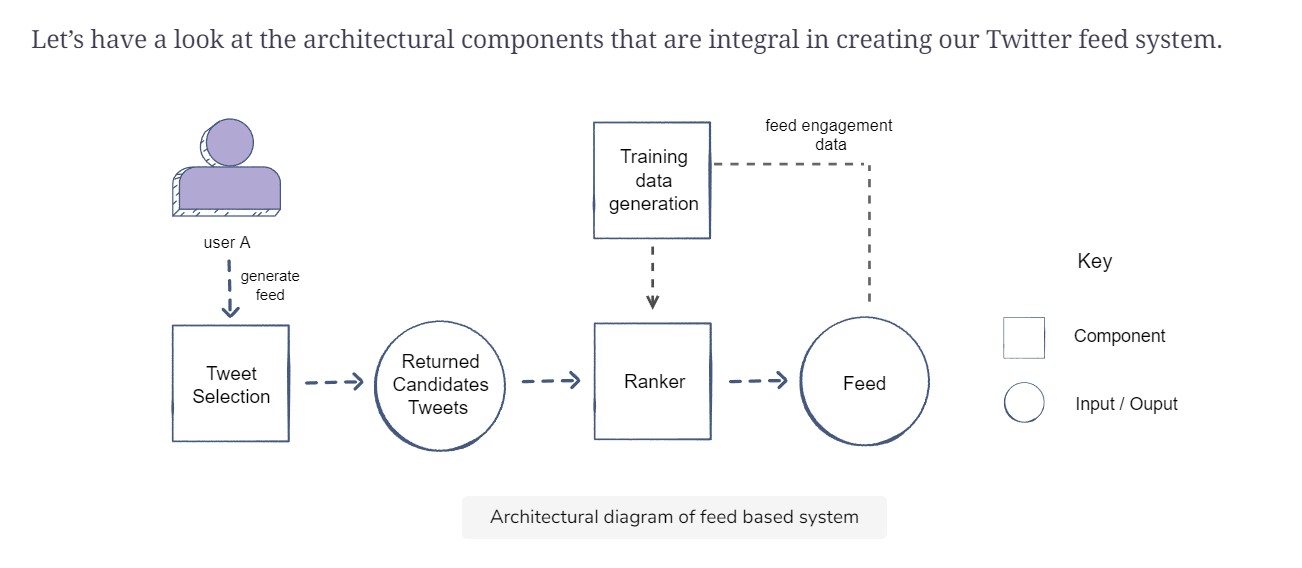
Architecture:
Continuous Integration:
- Version Control –> Git
- Automated TEsting –> Pytest, pytest-cov, codecov
- Static Code Analysis –> Pylint, flake8, bandit
- CI server: Jenkins, CircleCI, Travis CI to automate build, test and validation process
Continous Delivery:
- Iaas –> Terraform
- Containarization –> Docker
- CD server: Kubernetes, ECS, Google cloud Run to automate deployment process
Continuous Testing:
- Unit Testing –> Unittest, Pytest, nose
- Integration Testing –> Robot Framework, Behav, PyAutoGUI to test integration with other models
- Load Testing –> Apache JMeter, Gatling, Locust to test scalability and perf of model.
- A/B testing –> Tensorflow serving, Kubeflow, sagemaker to deploy multiple versions and test against different user groups or scenarios
Example 1: Build a model with CI
- Setup code in GIT
- Write Unit tests using Pytest.
- Create CI Pipeline using Jenkins or Travis CI
- Configure pipeline to run unit tests automatically whenever repo changes
- Use code coverage tool like pytest-cov.
- Use code quality tool like pylint.
- Use code review tool like codecov to review and merge code changes.
Example 2: Deploying a bmodel with CD
1.
References:
- Chip Huyen Machine learning systems design
- How to build your own search ranking algorithm
- https://towardsdatascience.com/what-is-machine-learning-system-design-interview-and-how-to-prepare-for-it-537d1271d754
- https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-answer-any-machine-learning-system-design-interview-question-a98656bb7ff0
- http://patrickhalina.com/posts/ml-systems-design-interview-guide/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/learnmachinelearning/comments/uu5l9b/new%5Fml%5Fspecialization%5Fby%5Fandrew%5Fng/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/learnmachinelearning/
- https://huyenchip.com/machine-learning-systems-design/toc.html
- https://www.theinsaneapp.com/2021/03/system-design-and-recommendation-algorithms.html
- https://fall2019.fullstackdeeplearning.com/
- https://mlsystemdesign.github.io/
Youtube
- https://www.youtube.com/c/joshstarmer/videos
- https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCB3l7wGZMJ5BuQzOiz6aIqA/videos
- https://www.youtube.com/c/BrandonFoltz/search
- https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCbfYPyITQ-7l4upoX8nvctg
- https://www.youtube.com/c/Deeplearningai/videos
- https://www.kaggle.com/code/vonneumann/benchmarking-sklearn-classifiers/notebook