Designing Search Ranking System
Overview of Search Rank Chapter from educative.io and other sources:
Problem: Design a search rank system for a search engine
- Clarify the following:
- Scope of the problem
- Scaling factors
- Personalization aspects
Identify the metrics:
-
Online Metrics: (Applicable per query)
-
Click through rate: \[ \text{Click Through Rate} = \frac{\text{Number of clicks}}{\text{Total Number of views or impressions}} \]
-
Sucessful Session Rate
-
Time to Success
-
-
Offline Metrics:
- Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG)
- Cumulative Gain is the sum of all document relevance
- Discounted Cumulative Gain penalizes incorrect relevancy of the document based on ground truth. (Ground truth is actual relevance as rated by human raters)
- DCG can’t be used to compare the search engine’s performance across different queries on an absolute scale. The is because the length of the result list varies from query to query. So, the DCG for a query with a longer result list may be higher due to its length instead of its quality. To remedy this, you need to move towards NDCG.
- NDCG is calculated by dividing DCG with max(DCG) or by calculating ideal DCG. IDCG is calculated by rearranging search results as per human raters.
- Average NDCG across N queries
- Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG)
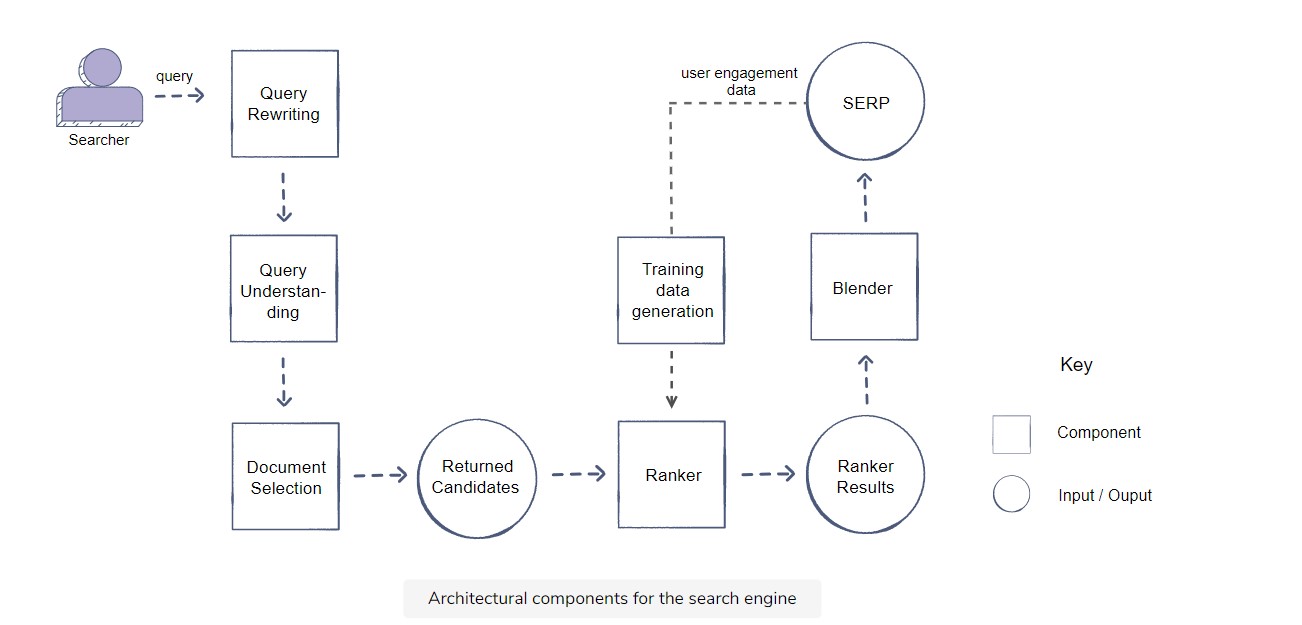
High Level architecture
- Two step process:
- Document Selection
- Filtering and ranking relevancy
Document Selection:
- Four actors:
- Searcher: prior query results, historical engagement
- Actual Query
- Document corpus
- Context
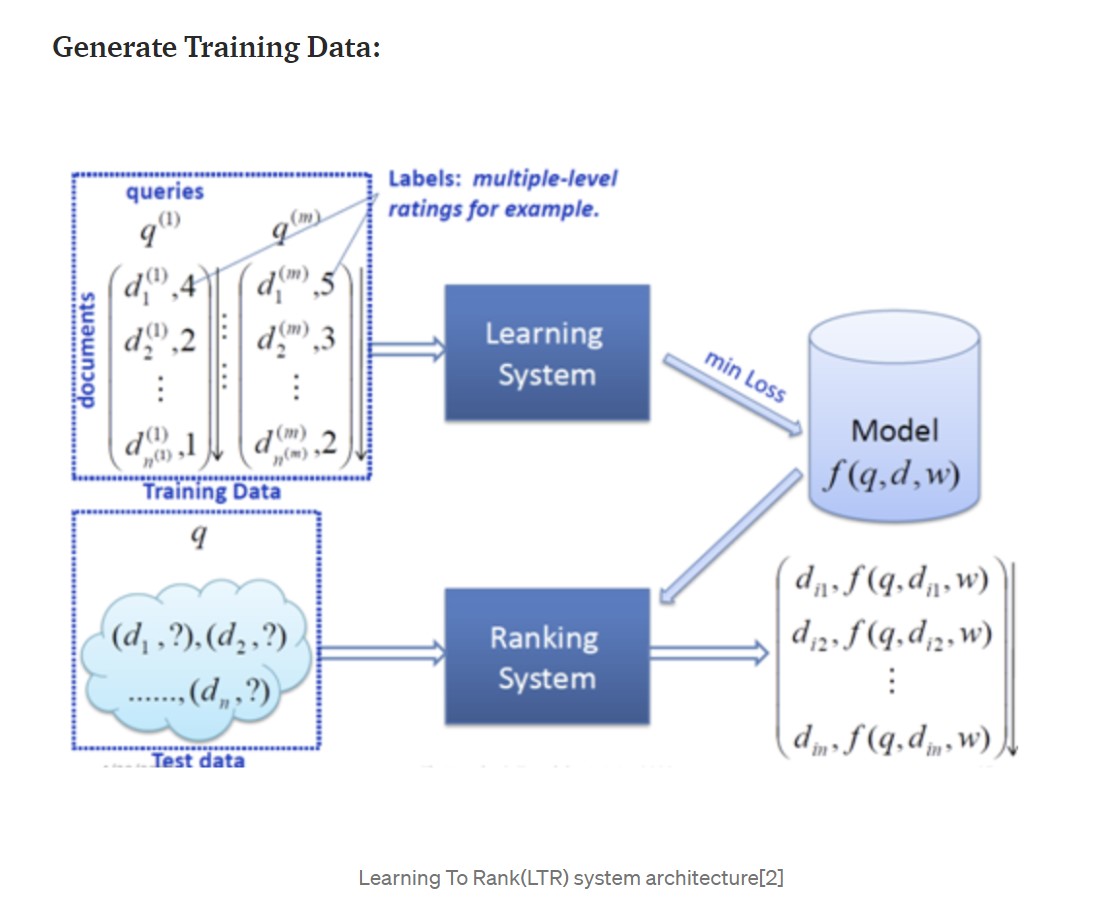
Overall approach for collecting documents for training:
- Collect a large number of (randomly extracted) queries to form a test set.
- For each request q- Collect the documents {dj} m j = 1 associated with the request.
- Take the judgment on the appropriateness of each document through a human evaluation.
- Use a ranking model to rank the documents.
- Measure the difference between the results of the ranking and the assessment of appropriateness using an evaluation measure.
- Use the average measure for all queries in the test set to evaluate the performance of the ranking model.
Query Processing:
- Lexical Based: Spell check, expansion, relaxation (removing stop words, helps to improve recall), translation (another form of rewriting text translation applied to convert tail queries into head queries which inturn helps recall), normalization (Stemming, unicode standardization, removing accent, spell checking and tokenization) etc.
- Graph based:
During query time, the query is parsed and tagged to the relevant concepts (i.e., nodes) in the knowledge graph. The query can then be expanded—to include relevant concepts—by finding the closest nodes in the knowledge graphs.
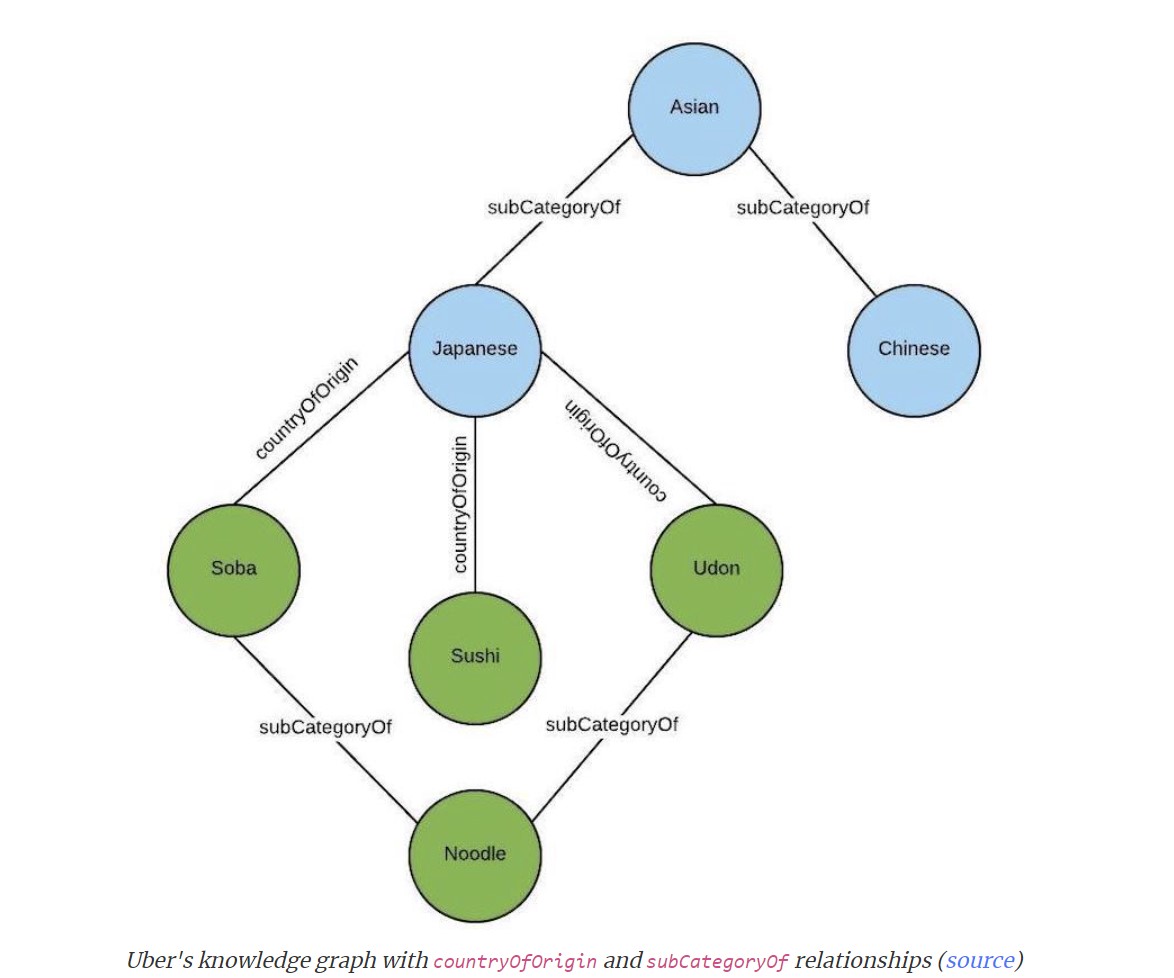
Both Lexical and Graph based approaches treat queries as bag of words and apply n-grams approach and struggle to understand synonyms, antonyms, morphological variants, spelling errors etc. Knowledge graph requires lots of manual work, huge effort to build the ontology and graph management.
Embedding based approaches require large behavioral data and is a problem with cold start.
- Embeddings Based
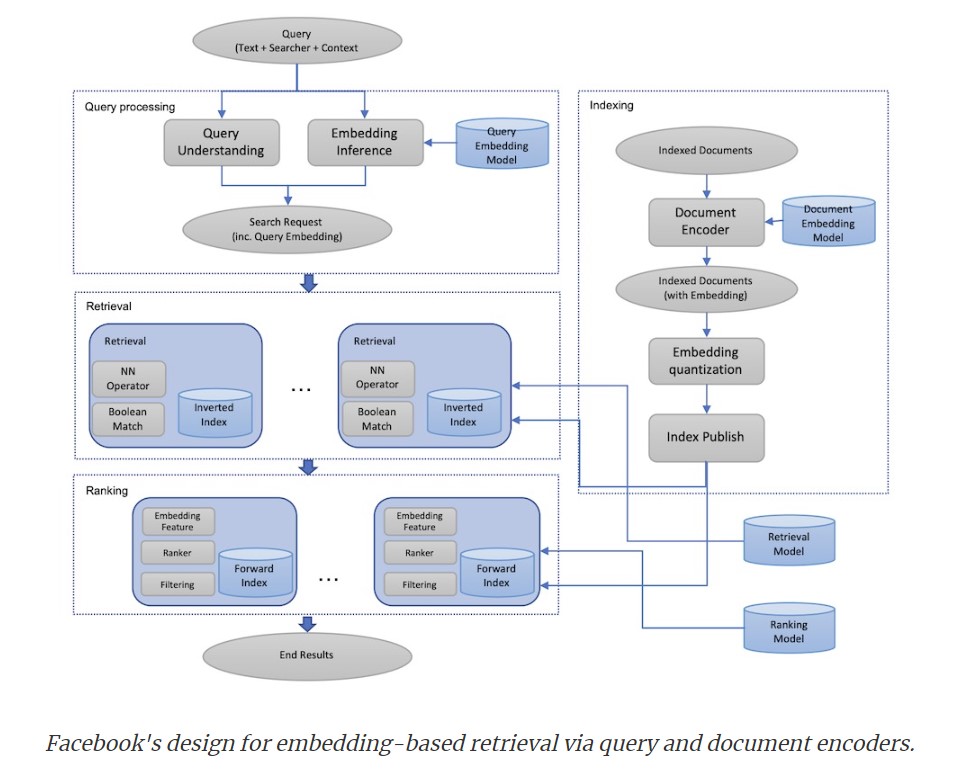
Embedding-based retrieval is a technique to use embeddings to represent query and documents, and then convert the retrieval problem into a nearest neighbor (NN) search problem in the embedding space
Scaling Challenges
Document retreival layer has millions of documents to consider against a given query unlike the ranking layer which has to deal with only 100s of document results.
Building embeddings for these millions of documents and searching against them introduces lots of scaling challenges.
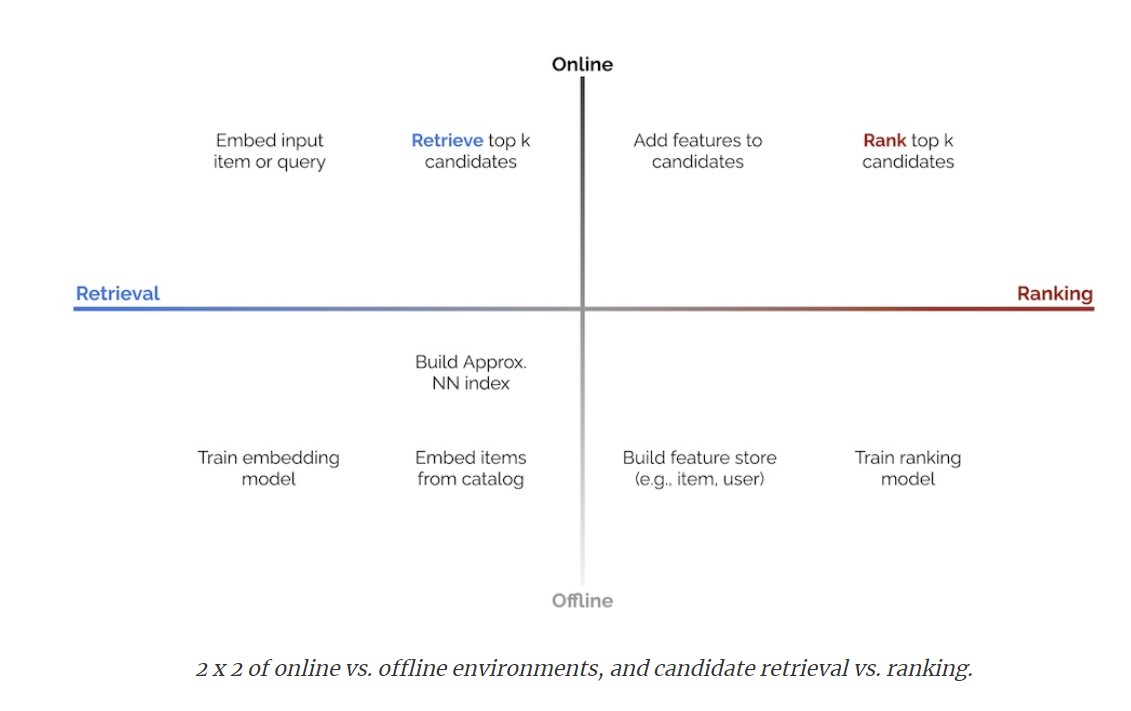
Learning to Rank:
-Feature based ranking:
- BM25
- VSM
- Latent Semantic Indexing
- Language Model for Info retrieval - LMIR
- PageRank, TrustRank and Query-dependent Page Rank models
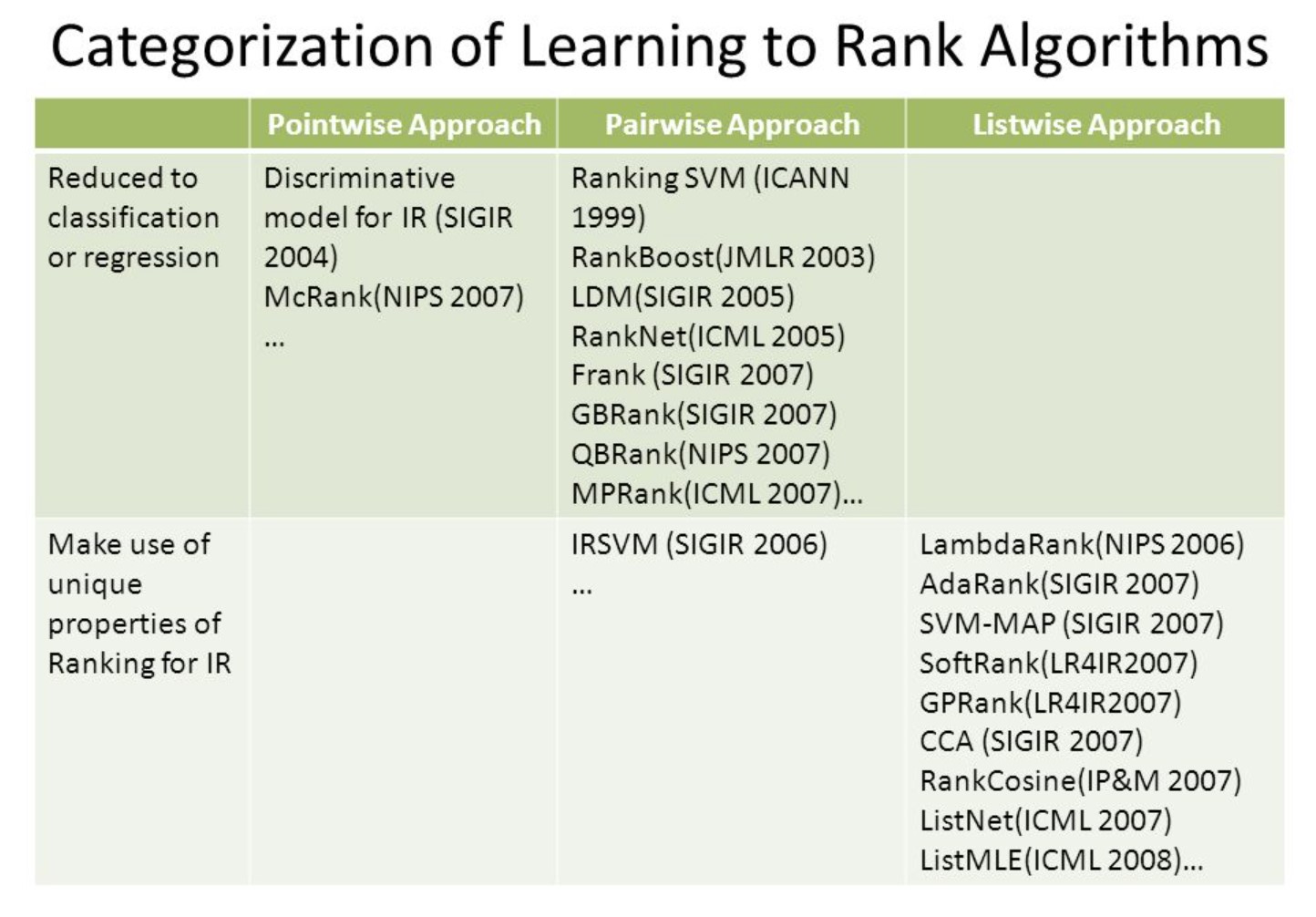
Machine learning approaches to ranking:
- Pointwise Ranking
- Pairwise Ranking
- Listwise Ranking
References:
- How to build your own search ranking algorithm
- System Design for recommendations and ranking
- Learning to retrieve and rank
- Search Engine ranking models - ultimate guide
- Explanation of learning to rank
- System design for search and recommendation
- From RankNet to LambdaRank to LambdaMART
Topics/Concepts to learn:
-
Query Rewriting:
- Stemming
- Lemmetizing
- Normalization
- SpellChecking techniques
- Tokenization
-
Embedding:
- Skip-gram approach
- CBOW
- Word2vec
- Glove Algorithm
-
Metric:
- Jaccard Similarity
- Cosine Similarity
- NDCG
- Pointwise Mutual Information Matrix
-
NN architectures:
- Transformer
- RNN
- LSTM
- GRU
-
Ranking Approaches:
- Pointwise Ranking
- Pairwise Ranking
- Listwise Ranking