System design concepts
Sharding
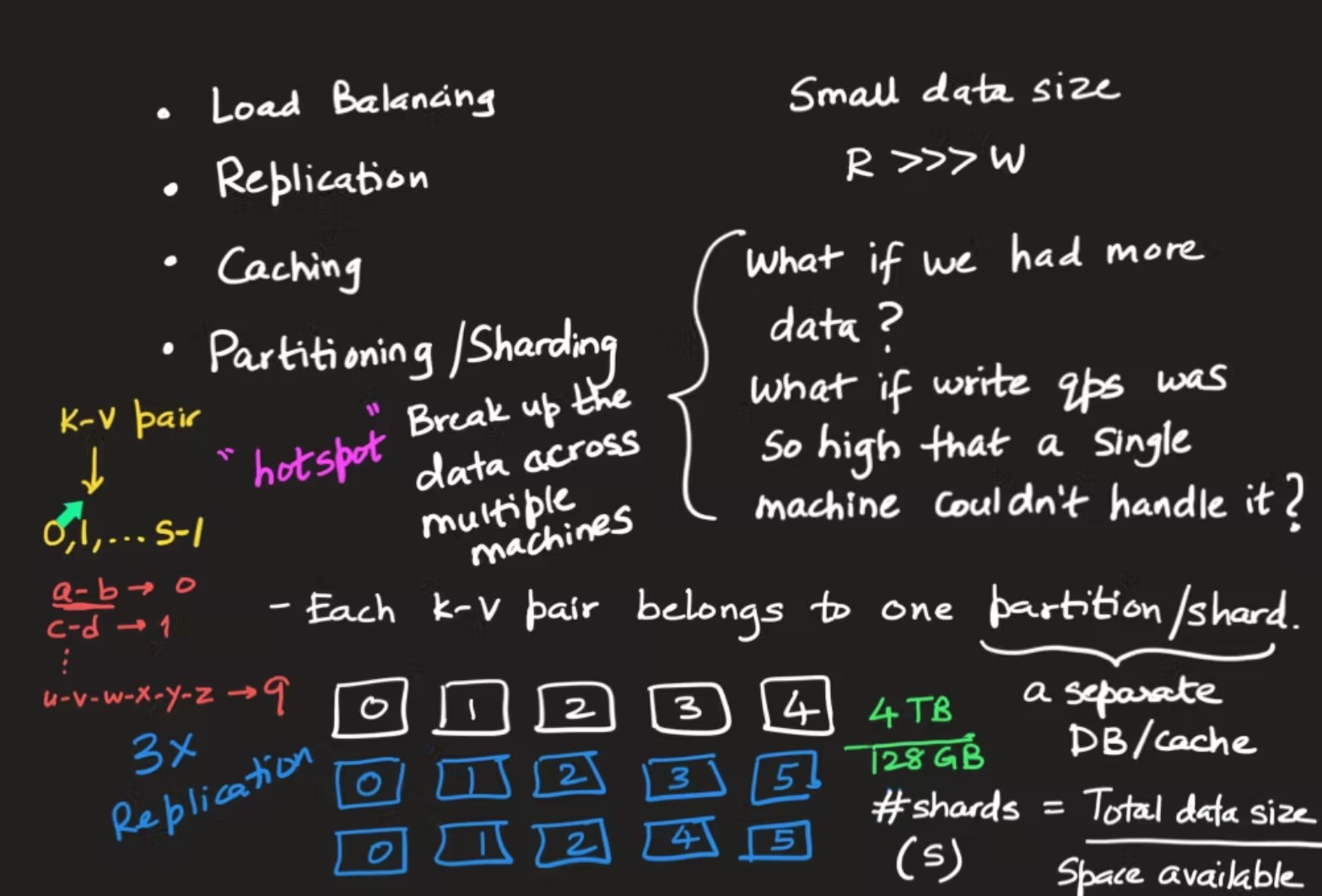
- What if we have more data in data tier? than app and cache tier?
- What if we have more write ops than read ops?
We would then need to divide/partition/shard the data.
- Each key-value pair belongs to one shard. Each shard is a separate
database and has separate cache. To keep availability high, each shard has to be replicated using the same replication schemes.
- To calculate # of shards, one approach is:
\[ \text{# of Shards} = \frac{\text{Total data size}}{\text{Space available in commodity server}} \]
-
How to map key value pair to a specific shard?
- We have to keep query load to be distributed as well as data size distributed.
- Otherwise some shards may be getting disproportionate amount of
traffic. This skew is called
hotspot. - We need unpredictable but deterministic approach to assign k-v pairs to shard. A similar example is MD5 cryptographic hash function.
-
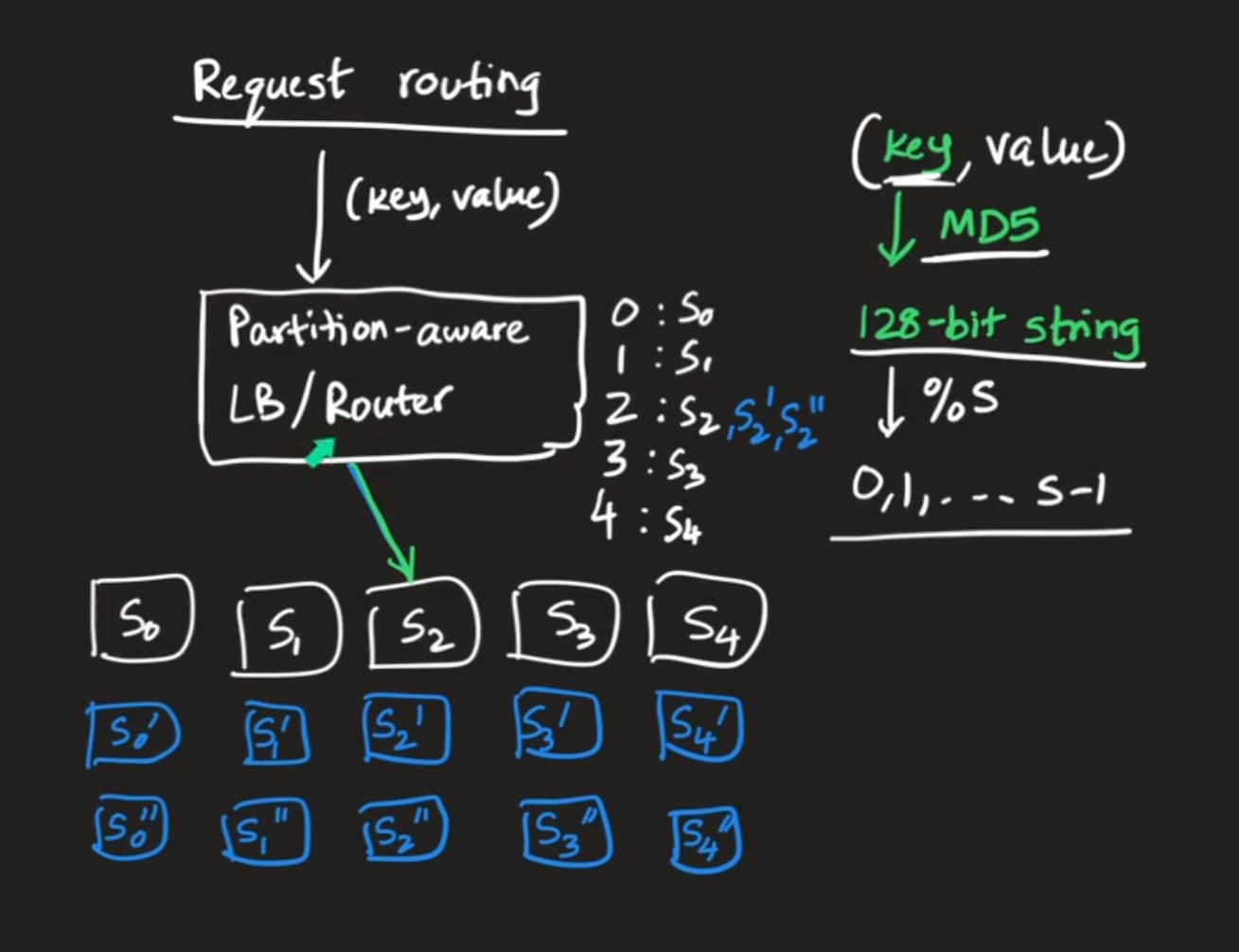
Request routing:
-
When a request comes in with a key, a partition aware router knows which shard server the key belongs to and its ip address. If the database is sharded and replicated, then partition aware router can do some load balancing while routing the request to a specific replica of shard server.
-
The partition aware router can do regular ping to the shard servers to check their health and accordingly route the future requests.
-
Resharding
- What if we do not know the # of shards upfront and if we need to incrementally increase shards?
- The hash function that uses # of shards and key could change when
shards increased. This means data has to move from one shard server
to another and this is called restructuring or rebalancing or
resharding. This is very expensive operation. Every single key value pair has to be moved from one shard server to another and this will be of \(O(k)\).

Rules to shard horizontally vs vertically.
- Step 1: Know your bottlenecks.
- Do I have more users?
- Do I have unstructured data?
- Based on user ids, we can give range
- Do you want to move partial data from one place to another?
- Are we going to just append data or are we going to create new cluster and insert the data in this new cluster?
Microservices Architecture
Overview:
Applications can be architectured in a few different ways. The main two approaches are monolithic architecture and microservices architecture.
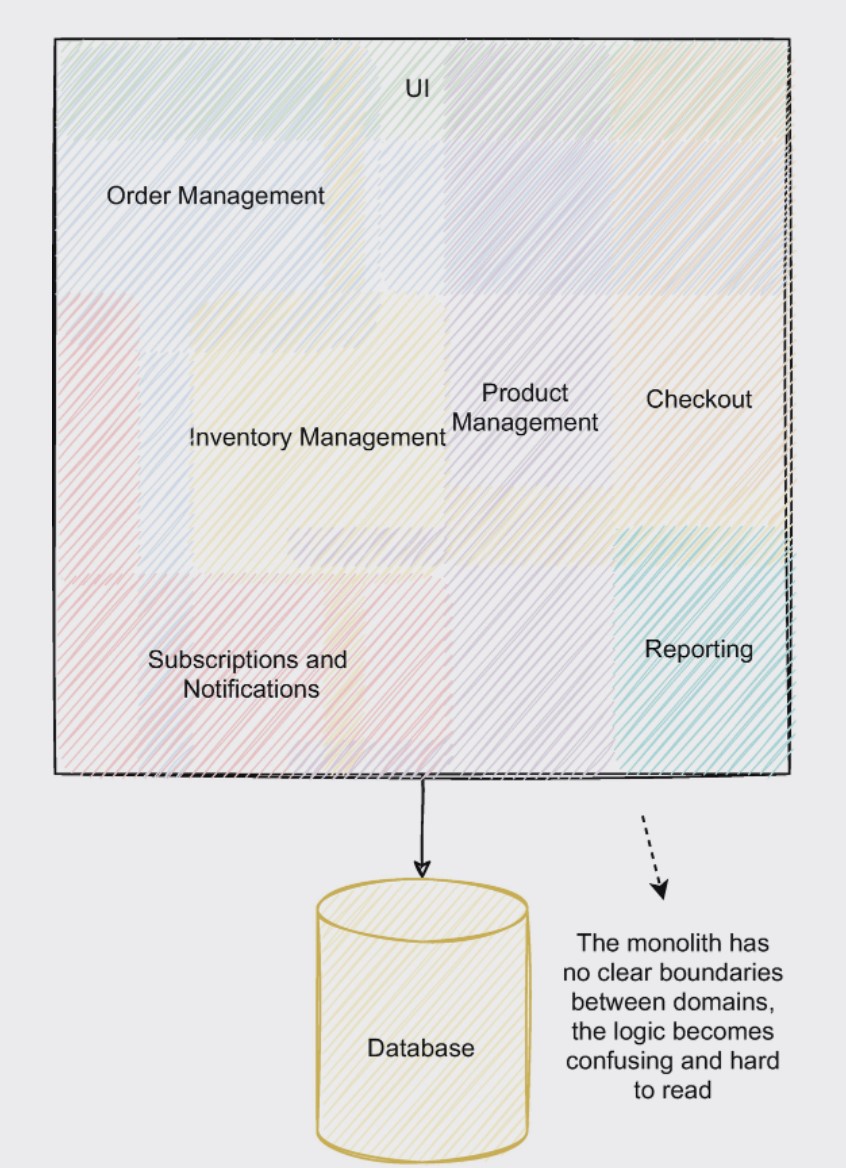
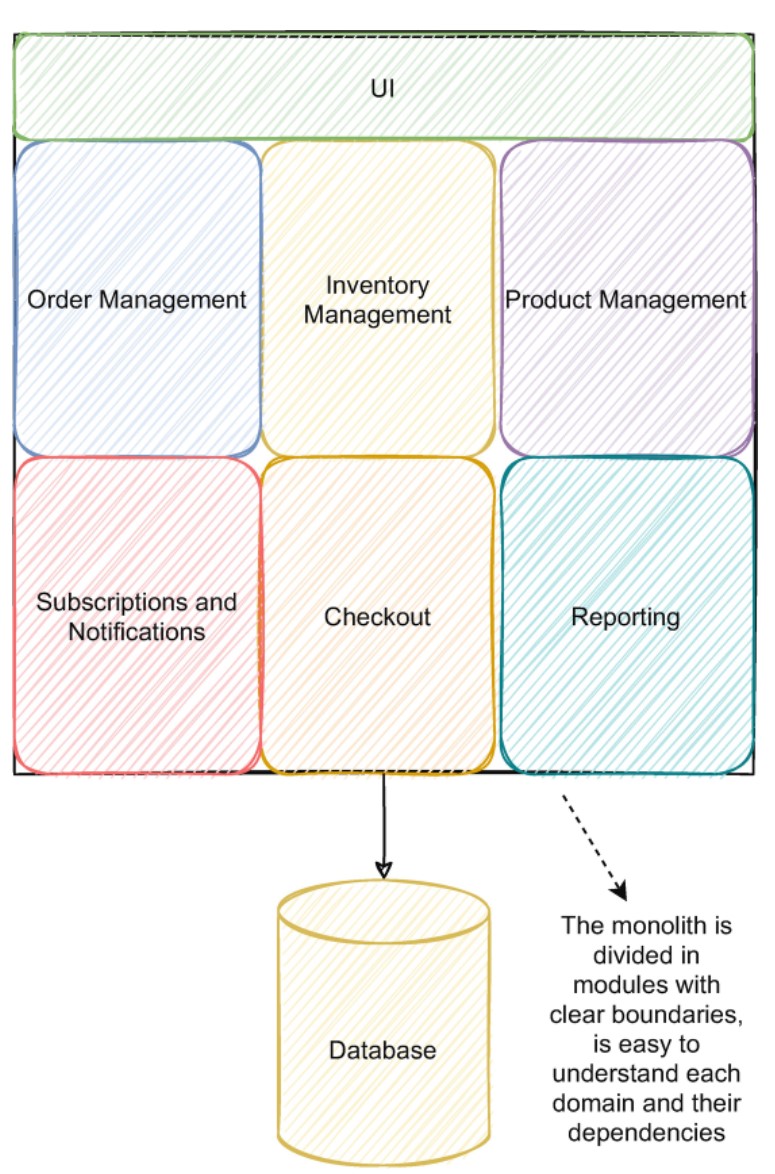
Monolithic Architecture
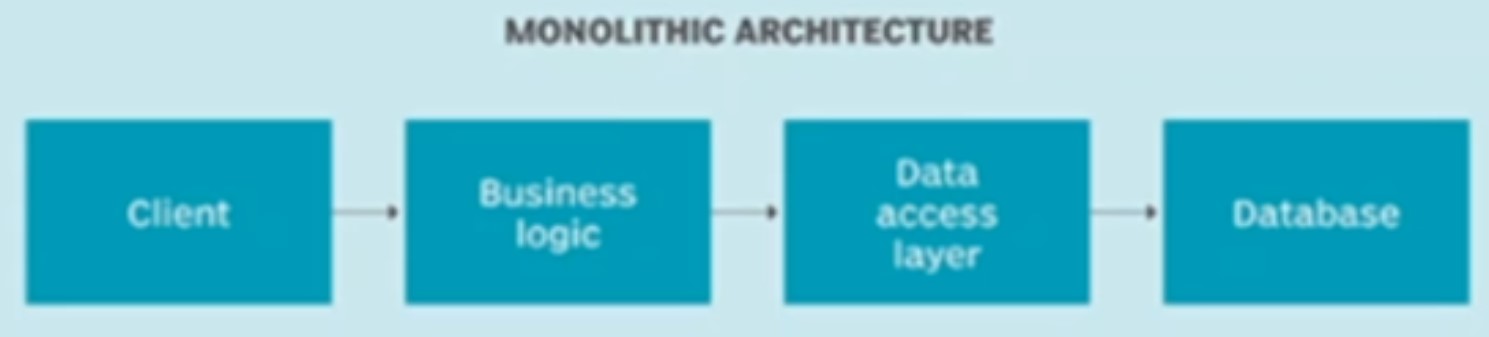
In Monolithic design, all of the business functionalities are clubbed together. For example, in an E-commerce application, payment service, notification service, user mgmt service, product service etc. all are clubbed together in one single app which in turn talks to the underlying database.
One advantage of this approach is that all services are in one name space resulting faster intercommunication and less configuration overheads
However, as the application scales, it becomes harder to maintain the codebase and clearly separate functionalities. Turnaround time for deployment goes up and overall product complexity exponentially increases.
Microservices Architecture
In microservices architecture, services that have different/independent business scope and functions are separated into independent services with its own technological stack.
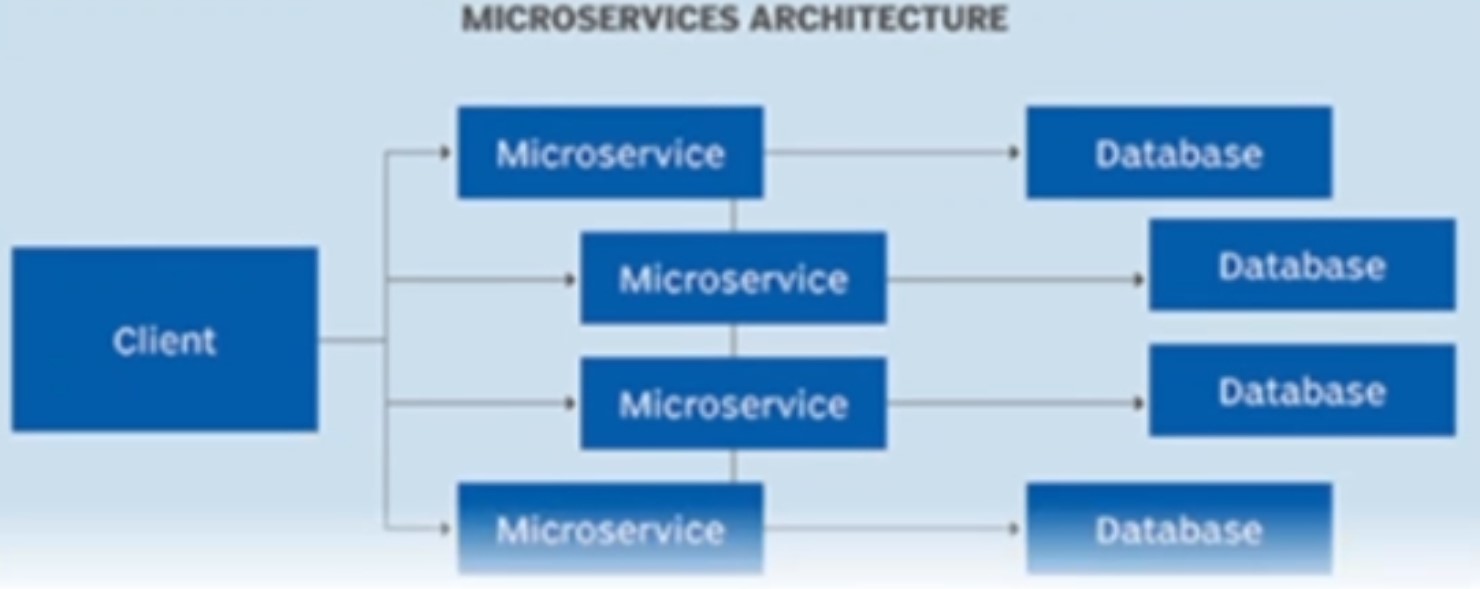
Some of the characteristics of this architecture are:
- The individual microservices have its own technological stack, including DB and DB mgmt model.
- The services communicate with each other using REST API, event streaming and message brokers
- The services are based on business functions.
- The services are usually small, loosely coupled, and can be deployed independently.
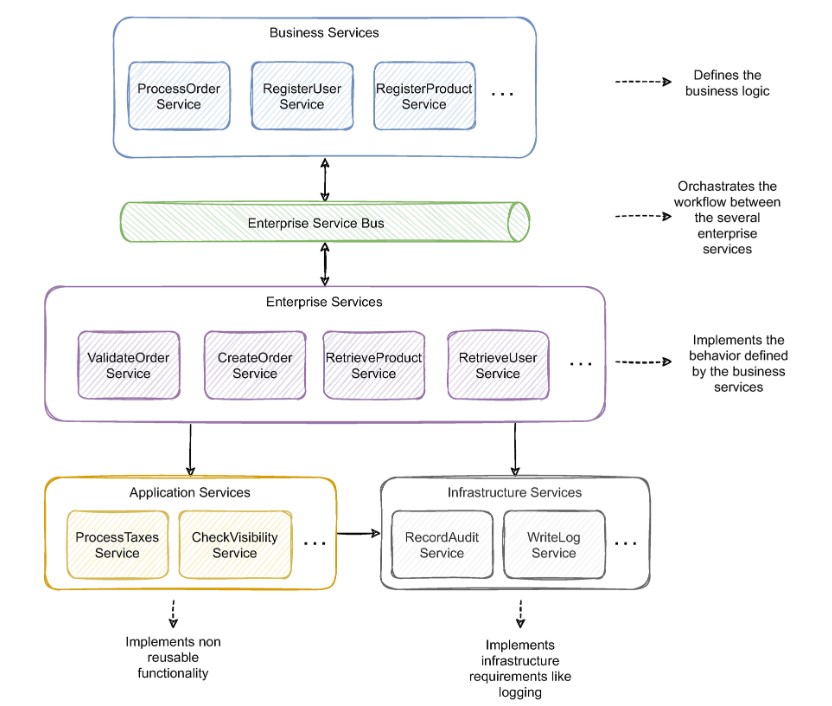
Components of microservices architecture
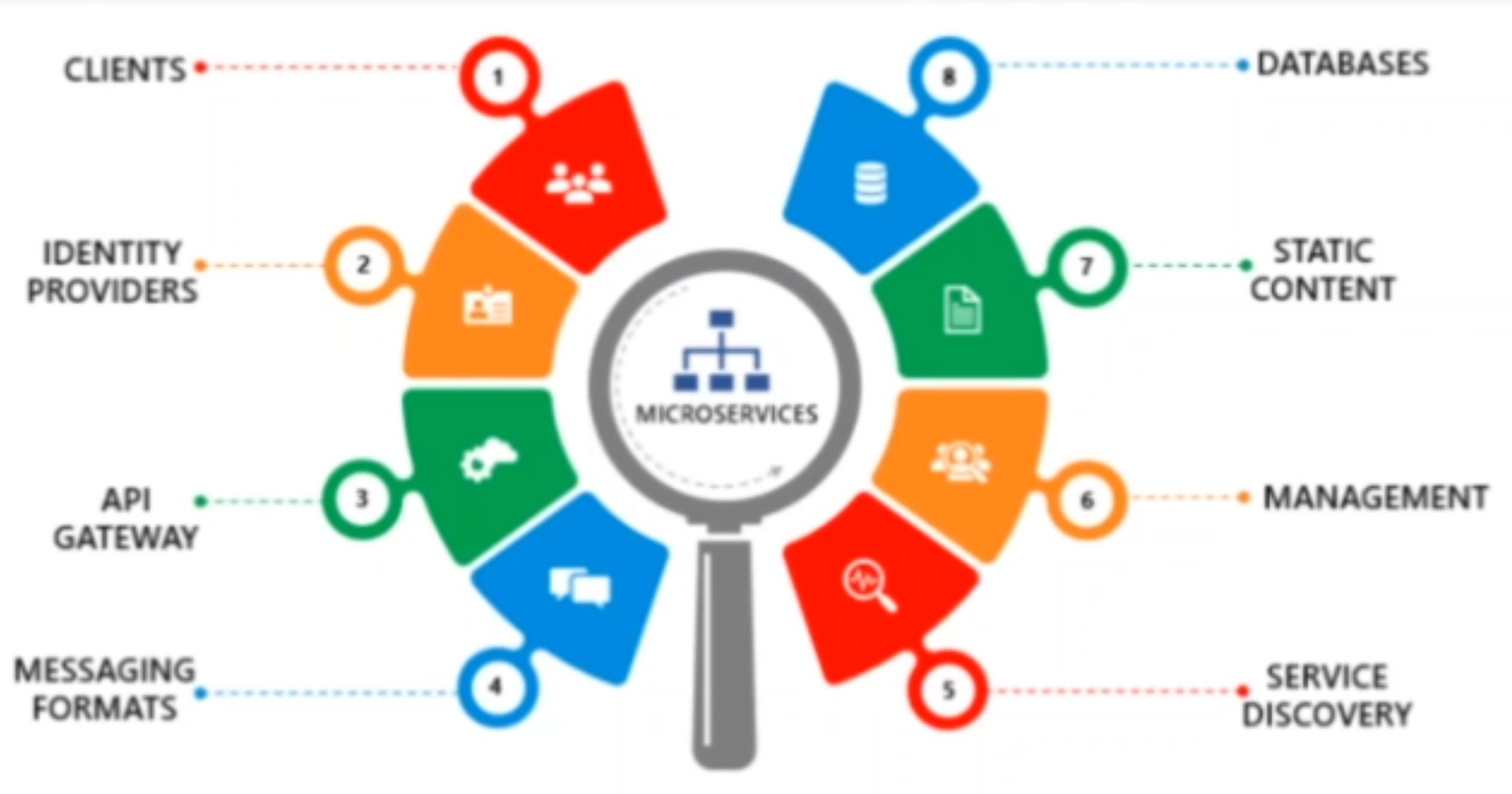
There are mainly 8 components in microservice architecture:
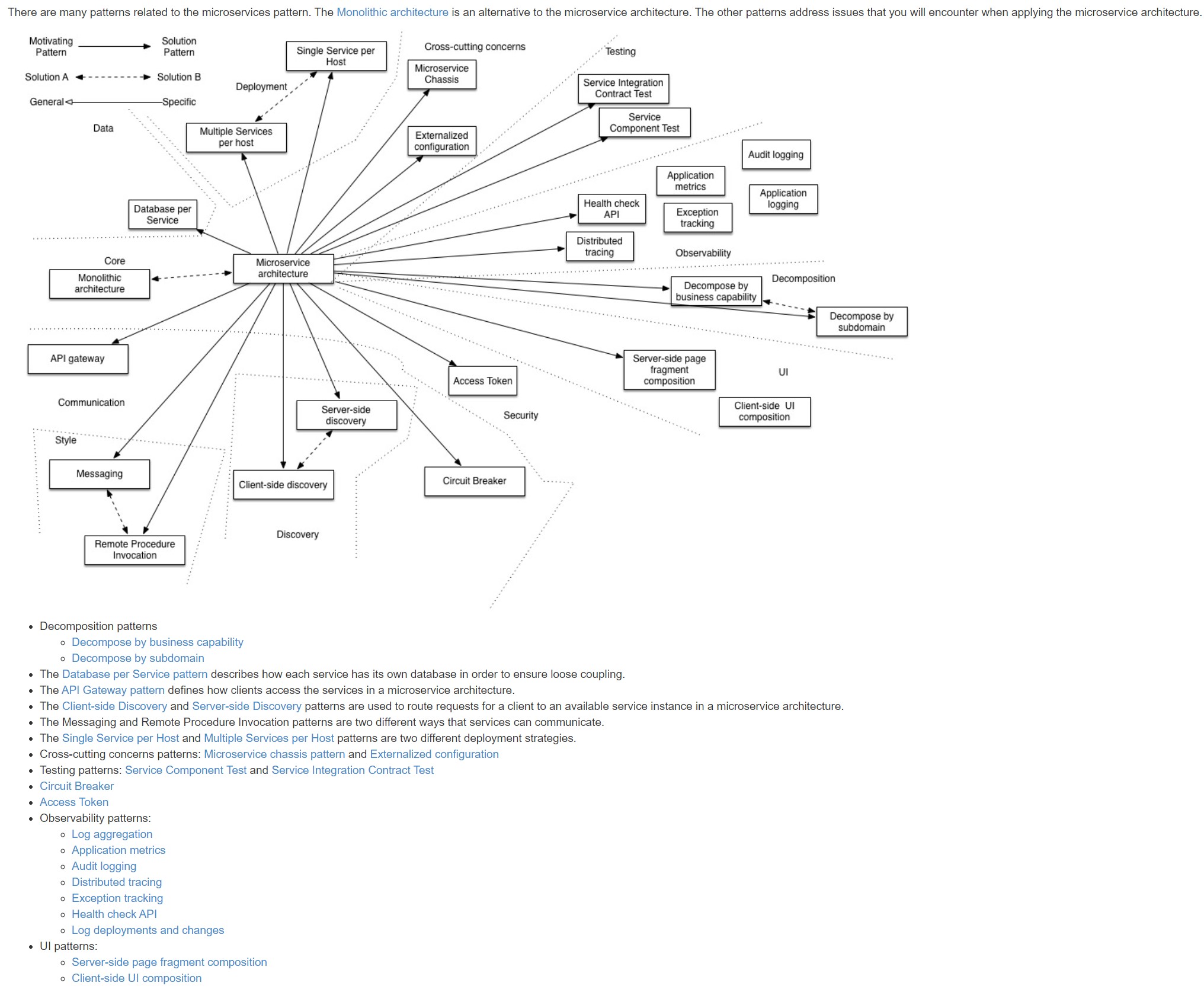
Patterns
-
Client: Can be a mobile app, chatbot, desktop app etc.
-
Identity Provider: allows to authenticate/authorize the client. Provides access management solution
-
API Gateway:
- Provides entry point for the client.
- Forwards requests to different microservices. Client makes call via URL and
- API gateway has the mapping knowledge of url to specific microservice componenet and routes it accordingly. This provides backend abstraction and clients can be managed without exposing to
client.
- API gateway can also add as load balancer.
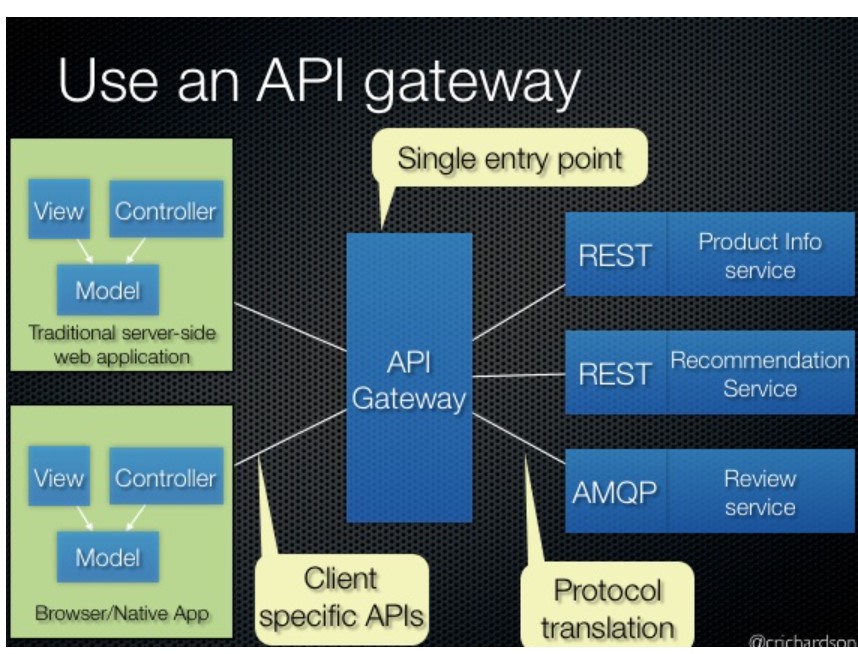
-
Different clients may have different needs of data. API gateway provides this abstraction
-
The API gateway handles requests in one of two ways. Some requests are simply proxied/routed to the appropriate service. It handles other requests by fanning out to multiple services.
-
Rather than provide a one-size-fits-all style API, the API gateway can expose a different API for each client. For example, the Netflix API gateway runs client-specific adapter code that provides each client with an API that’s best suited to its requirements.
-
The API gateway might also implement security, e.g. verify that the client is authorized to perform the request
Service Discovery
- Service instances can have dynamically assigned network locations and because of various factors such as autoscaling, failover and upgrades the service instances change dynamically. The service location is no more static and this is where service discovery helps.
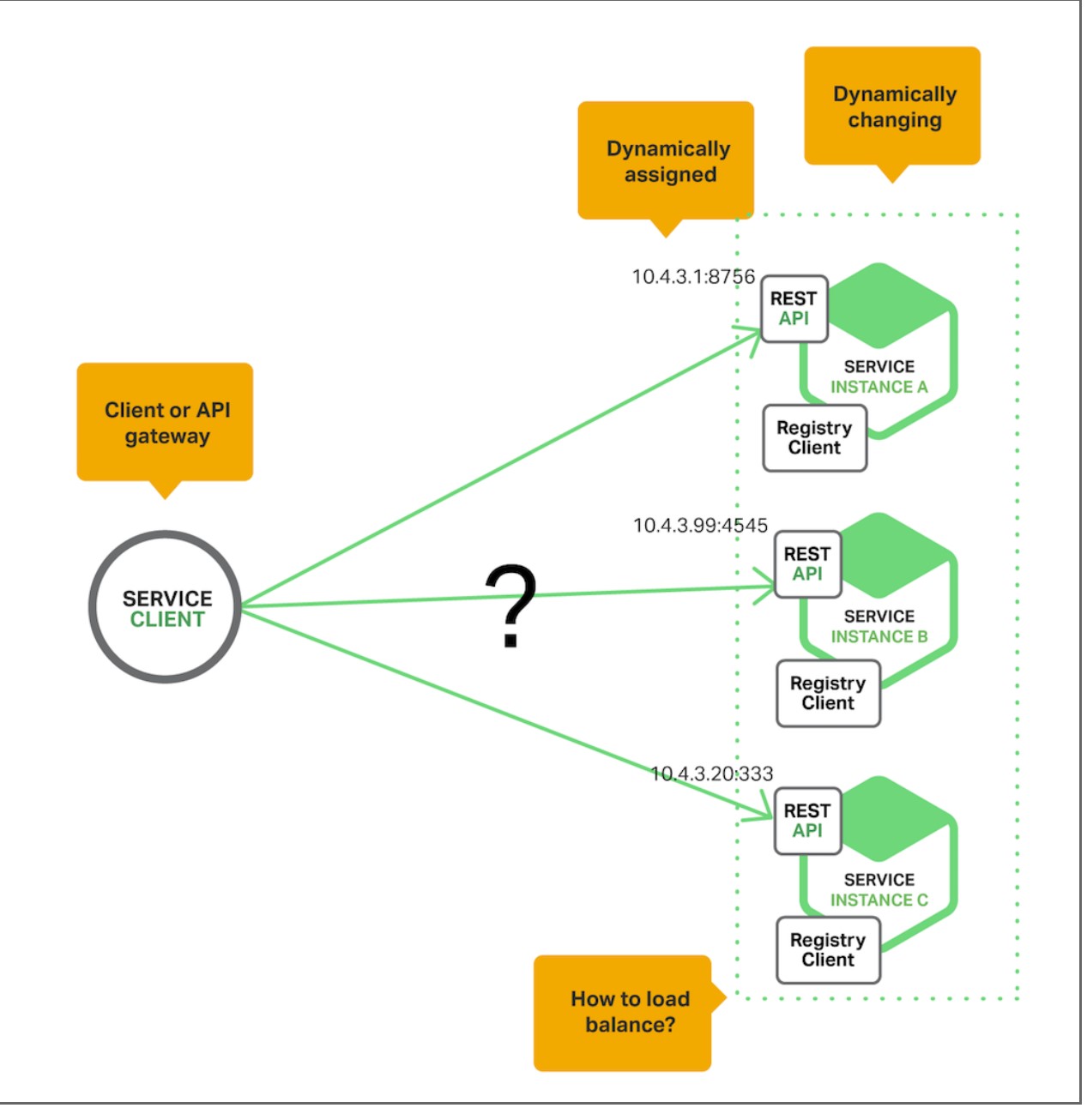
There are two types of service discovery patterns:
- Client side discovery: The client queries the service registry which is a database of available service instances. The client then uses load balancing algo to select one and makes a request.
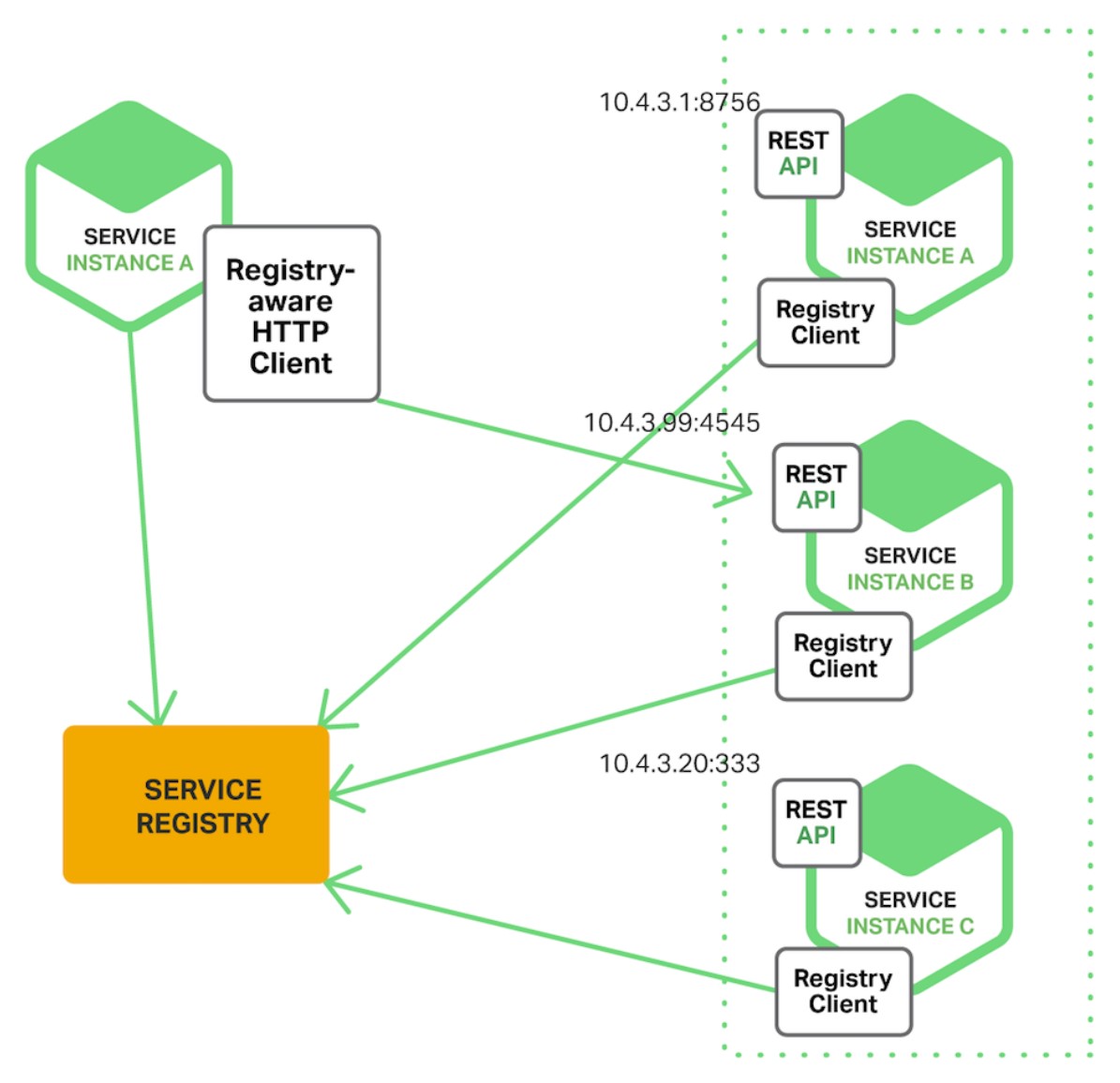
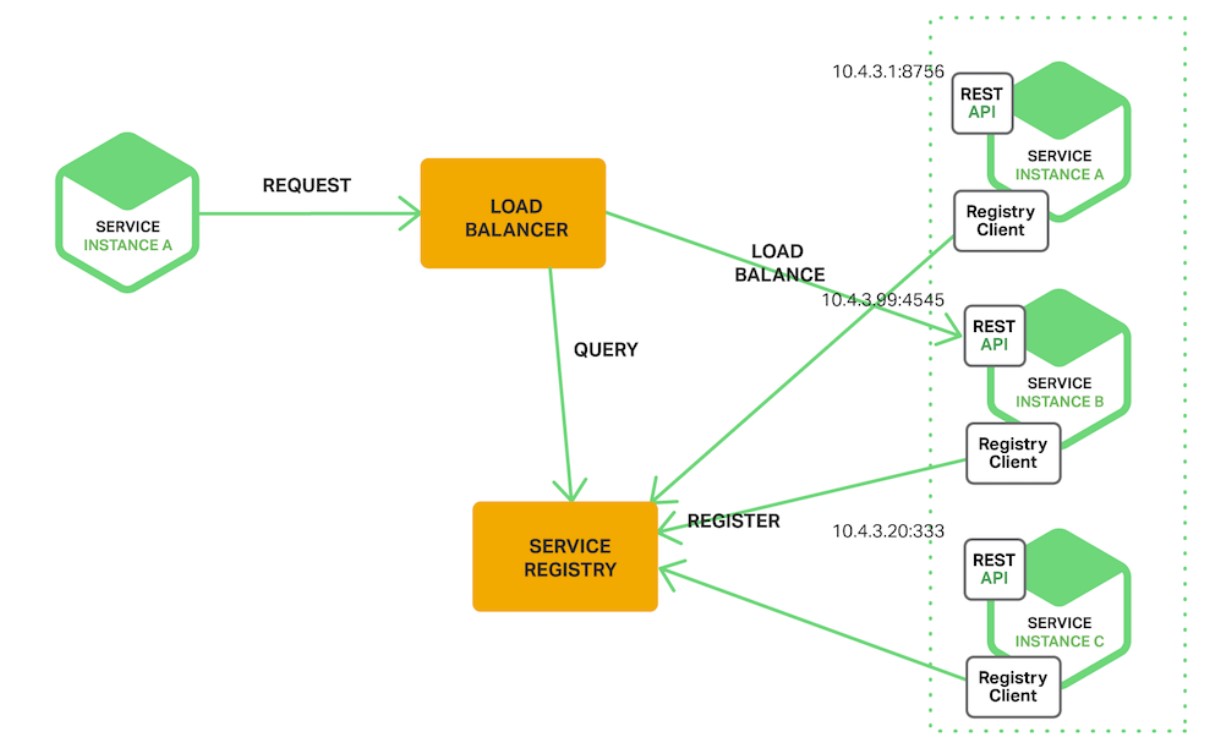
- Server side discovery: The client makes a request to the load balancer which inturn queries the service registry and routes the request to an available service instance. Service instances are registered and deregistered in service registry. Example: AWS Elastic Load balancer.
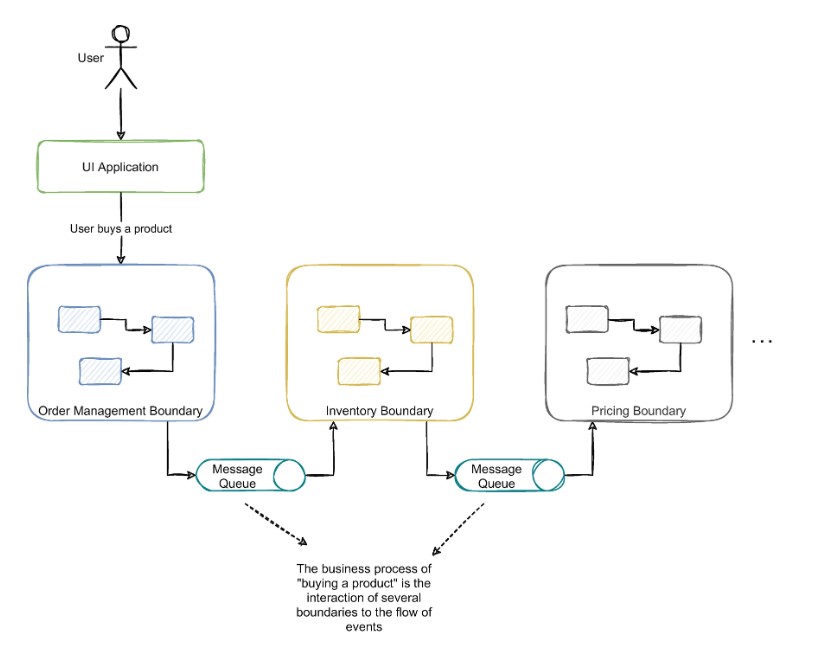
Event Driven Architecture
- The characteristic of EDA is loosely coupled components and services.
- Small scale EDA can be implemented directly between the services. Another option is to have a mediator in between the service and subscribers. Or having an event bus in the middle.
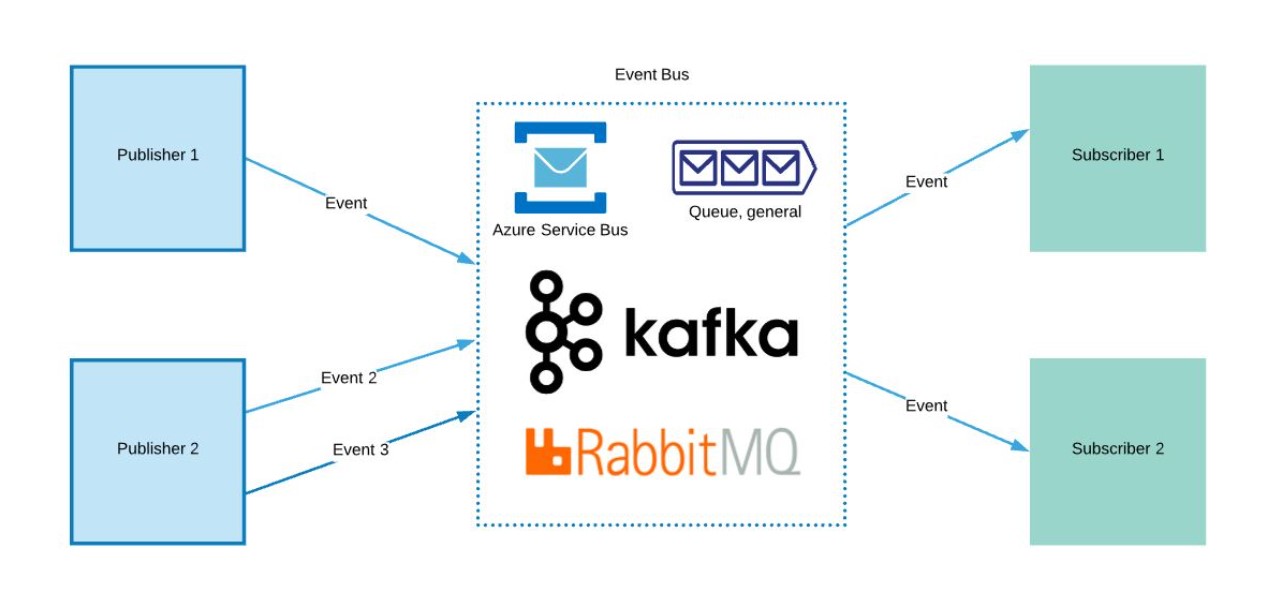
- The Event Bus can be based on the following components:
- Azure Queue
- Azure Service Bus
- Apache Kafka
- RabbitMQ
The choice is based on the scale of the events, and architectural complexity.
| Monolith | Modular Monolith | EDA | SOA |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
If you have million items, how can a user find what the user needs?
This is called product discovery. The second problem is to ship the product within in SLA. Align inventory and order fullfillment. How does suppliers improve their sales? Reports and marketing insight.
Q. What are the issues if the consumer thread is multithreaded and reads from the partition in parallel?
- Checkpionting becomes more complicated
- hard to preserve orders.
- Mechanism of avoiding double counting. (if the same message is submitted to partition multiple times, double counting can happen. One approach is to use a distributed cache which maintains a unique identifier and it can remove duplicates if multiple same messages arriave within a time threshold.
Step by step guide for System Design: questions to ask interviewer:
-
Users/Customers:
- Who uses the system?
- Per hour stat only for owner?
- How will the system be used? only one dept?
- Is data used in realtime
-
Scale (read and Write)
- How much data is coming and retrieved?
- How much data QPS?
- Should we deal with sudden traffic spikes?
-
Performance
- Should we do batch or stream processing?
- How fast data mustbe retrieved…or response time? IF response time is small, then minimum processing while reading and aggregration happens in write.
-
Cost
- Open source framework
- Maintenance means public cloud
Design a video view count service:
HLD:
- A db to store data
- Web server to process incoming video view events and store in db.
- to retrieve view count, another service is introduced.
Start with defining a data model:
- Shoudl we store each indiviudal event
- or aggregrate data ( per minute) in real-time
pros and cons:
- individual event can be stored really fast
- can slice and dice data in all manners
- recalculate numbers from scratch.
- cannot read data quickly.
- when total is requested, we need to aggregate while reading
- more money to store more data
- aggegate data read is faster
- decision making in real time
- ability to filter or aggegrate differently is very difficult.
- Need to preaggreate in mem before storing in db
- hard to fix errors
ask interviewr:
- expected data delay
- mabe combine both approaches as needed. system becomes more complex and expensive
Where to store the data:
- evaluate both sql and nosql options
- How to make both reads and writes fast?
- HOw not to lose data in case of faults?
- How to achieve strong consistency? and related tradeoffs?
- How to recover data in case of an outage?
- How to ensure data security?
- How to make it extensible for data model changes in the future?
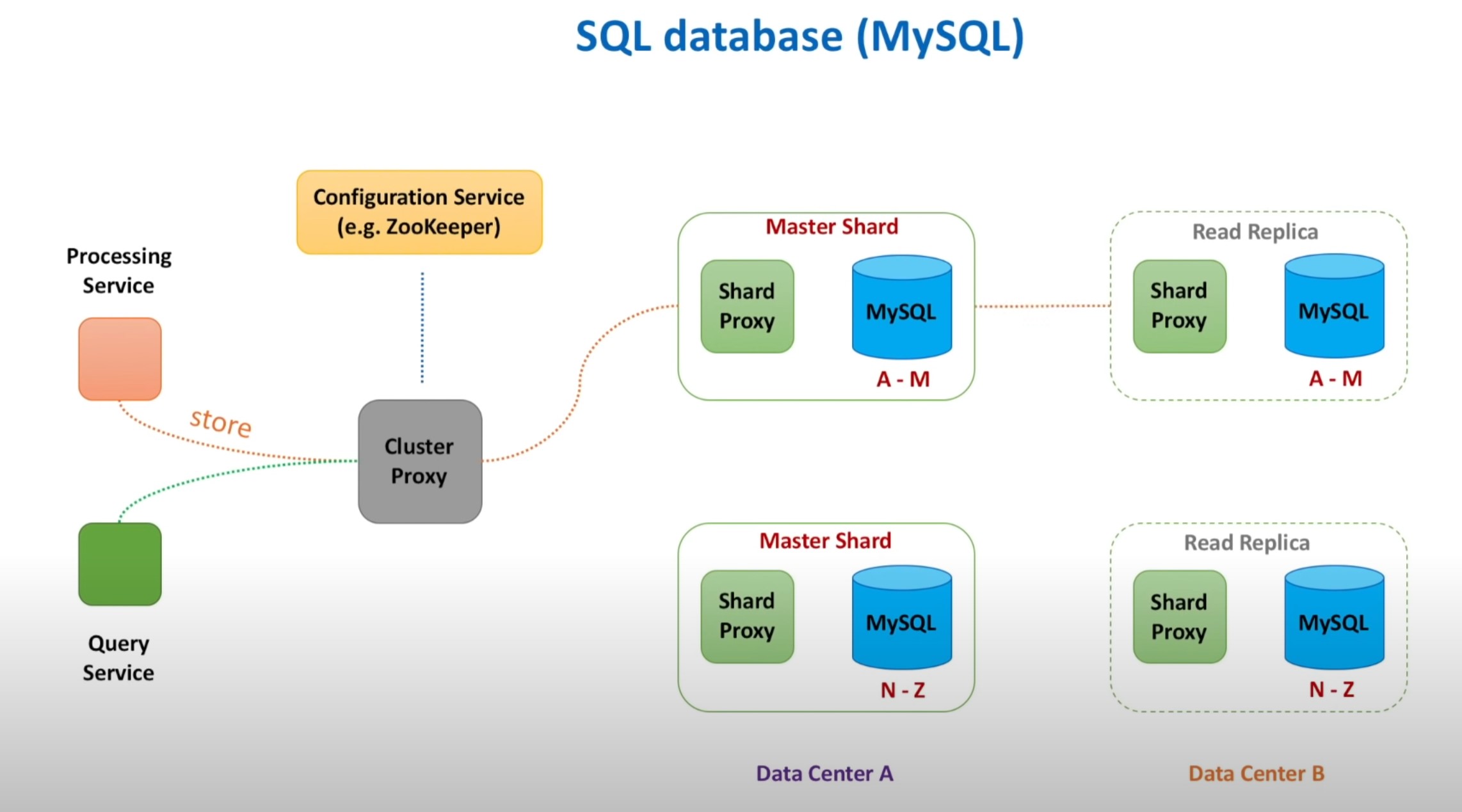
SQL DB:
-
Sharding or horizontal partition and requires many machines.
-
We need to know which machine stores and retrieves the data from it
-
A light proxy server can route to the requests to the right db and no need for the service to know each and every db.
-
Proxy needs to know if a shard dies or when a new shard is added… This can be done using a configuration service and it maintains the health via heartbeats.
-
Should this light proxy server (cluster proxy) directly call all the shards in different machines? One other option is to introduce a shard proxy. This can cache query results, monitor DB, publish metrics and terminate queries that take long time to retrieve data.
-
Scalability and perf. have been addressed. What about availability? What if shard dies? How to make data is not lost. For this we need replication.
Data Replication:
-
Keep one shard as the master shard. and create a copy or copies that act as read replicas.
-
The writes go via master shard and the reads can go to either master or follower shards.
-
The replicas can be in different data centers so if one datacenter goes down, we still ensure availability of data.
-
Data replication from master to followers can be done via synchronosly or async.
-
Youtube has implemented similar solution to scale large clusters of mysql instances. This is called
Vitess
Back of the envelope Calculations:
- Four types of estimations:
- Load or Traffic Estimates
- Write to Read Estimate: write to read ratio - 1:100 and 1M writes per day = 1M = 10^6 * 24 * 60 * 60 = 10^6 * 25 * 4000 = 10^6 * 10^5 = 10 req / sec So reads per sec = 1000 req/sec
- Database Storage Estimates
- To calculate storage estimate, we need to know how much is each write request and how long to store.
- if each write request is 1KB, and we have to store for 10 years, storage for 10 years = 1M requests and each request is 1KB and we have to store for 10 years = 10^6 * 10^3 * 4000 = 4 TB storage for one day = 1 Million requests * 1KB = 1 GB
- To calculate storage estimate, we need to know how much is each write request and how long to store.
- Load or Traffic Estimates
Design Topics
Design Tinder:
Functional Requirements:
- Store Profiles
- Images (maybe 5 images per user)
- Recommend Matches - # of active users
- Note Matches
- Direct Messaging
Services:
- Profile service
- Add profile
- Update Profile
Questions:
-
How are we going to store images?
- Should image be stored as file or blob (Binary large object) File - Cheaper, faster, and with static content, we can use CDN Database - Provides mutability ACID properties, access control and .
-
How is user authenticated in profile service?
- Instead of sending username passwd, send token.
- What happens when multiple services require authentication? Should all of them reach out to profile srevice?
- One solution is to use gateway. Client talks to the gateway and noone else talks to the gateway.
- gateway takes user inputs and checks with profile service about authentication status and routes the service and takes the response back to the user.
-
Where should be images be stored?
- In the same place as profile service or separately. Maybe have a separate image service which will have distributed file system to store images.
-
How one client can connect to another client via direct messaging?
- do not use client server protocol
-
Use peer to peer protocol - XMPP is one example
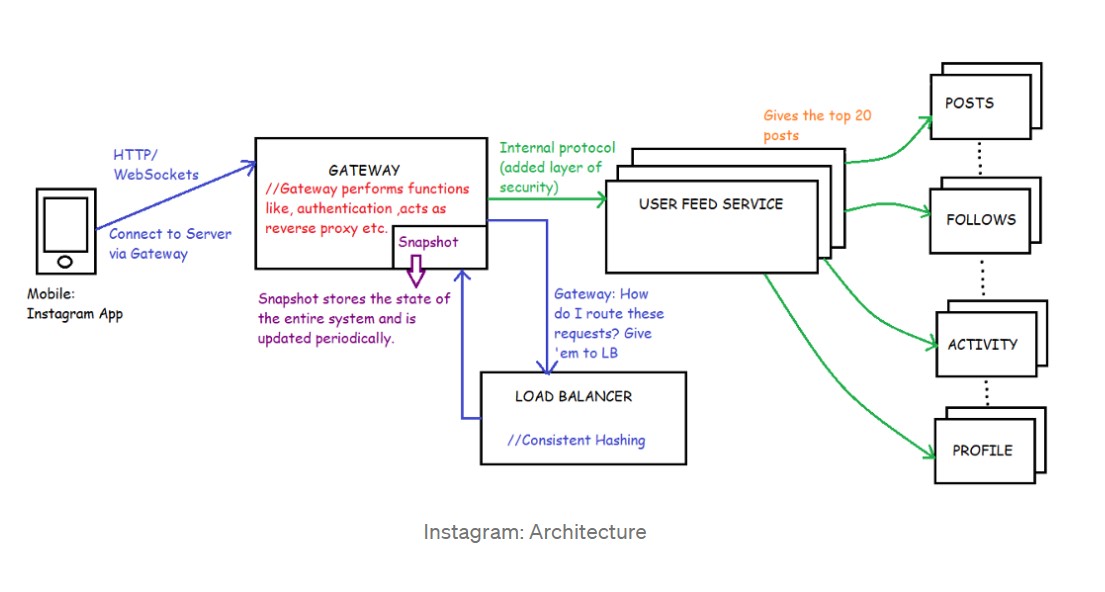
Design Instagram
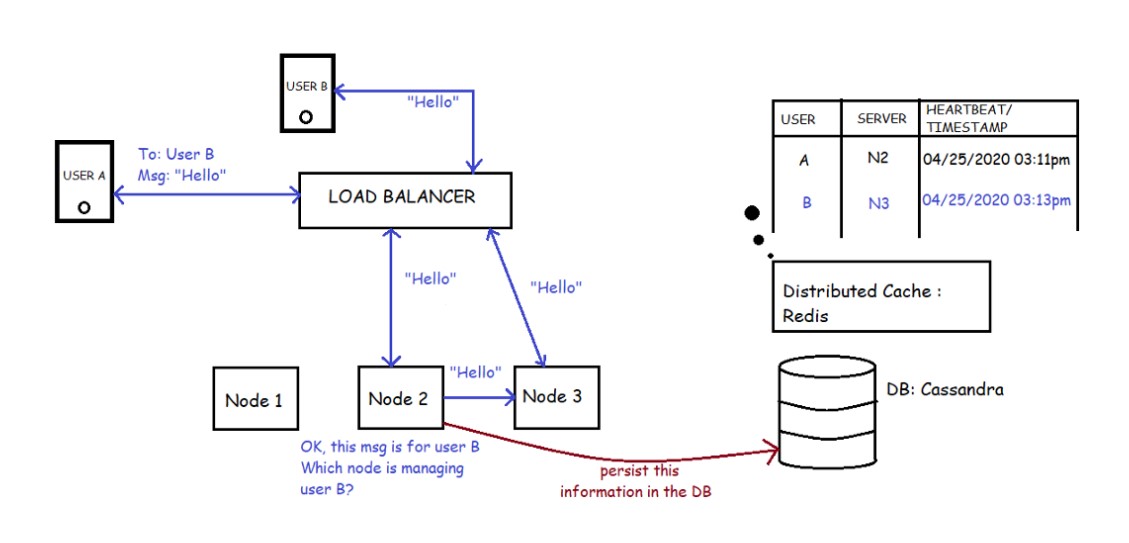
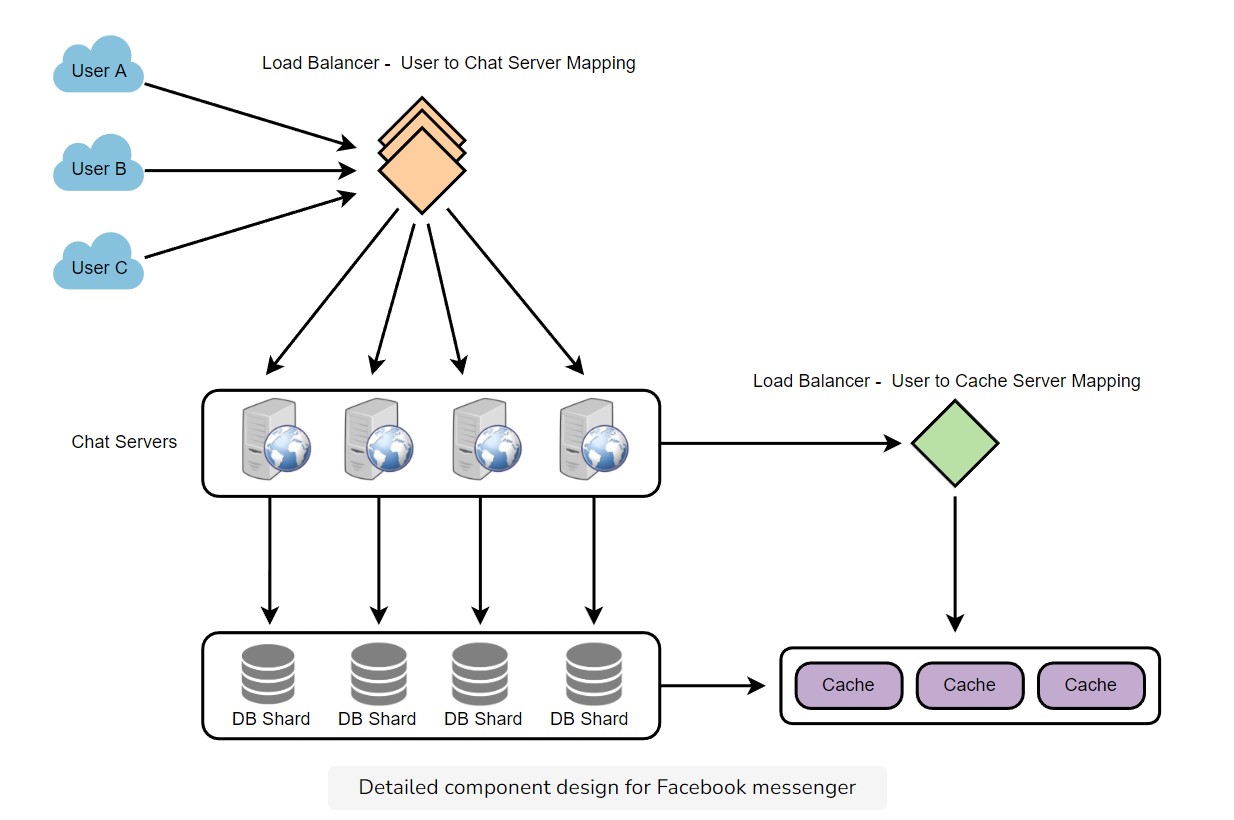
Design Messaging Service
| Design 1 | Design 2 |
|---|---|
|
|
Design NewsFeed Service
References:
- Narendra’s videos on System Design
- SDE Skills channel on System design
- Designing online game system
- Engineering MLOps
- System Design Donne Martin
- Designing a Web crawler
- System Design Tutorial from freecodecamp
- AirBNB Hotel Booking Design
Books: